Triggers
A trigger defines the event that starts a flow. This could be from an internal or external activity, such as changes to data, logins, errors, incoming webhooks, schedules, operations from other flows, or even the click of a button within the Data Studio.
There are 5 types of triggers: event hook, webhook, schedule (CRON), "another flow", and manual.
Event Hook
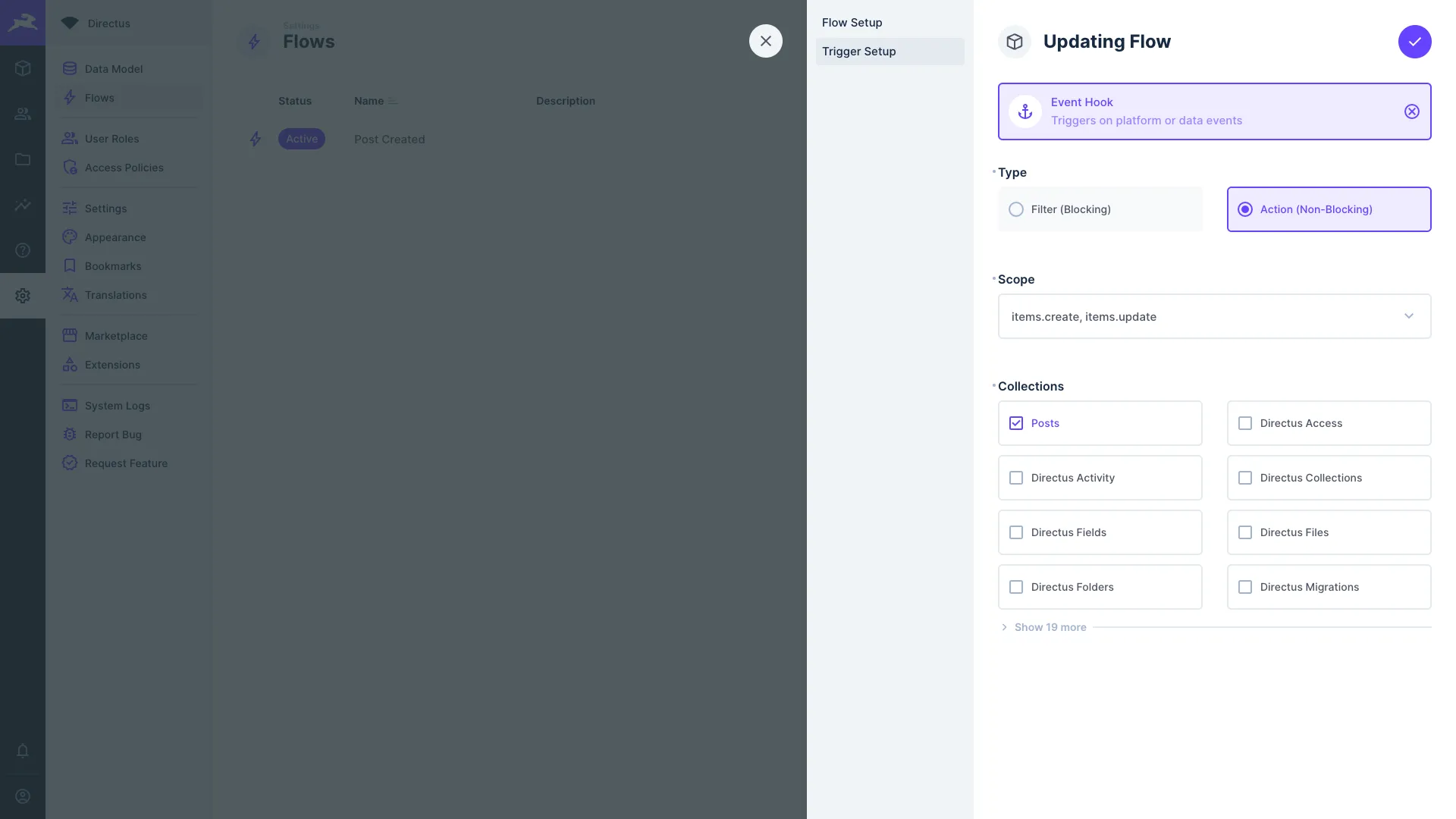
Event Hooks are triggered by events within the platform. The logic is based on Custom API Hooks.
Any data generated by the event will be nested in the $trigger.
- Type — Choose the type of event hook:
- Filter (Blocking) — This pauses the transaction and passes the
payloadto your flow, allowing you to validate or transformpayloador even prevent the event transaction. - Action (Non-Blocking) — Actions do not block the event. A non-blocking action is mostly useful for completing tasks in response to an event, without modifying the event or slowing the API.
- Filter (Blocking) — This pauses the transaction and passes the
- Scope — Set the types of events that trip this trigger.
- Collections — Set the collections whose events trip this trigger.
- Response Body — This is optional and only for "Filter (Blocking)" events. It defines data to replace the
event's original
payload. Choose to return:- Data of Last Operation — Replaces event
payloadwith value from$last. - All Data — Replaces event
payloadwith the entire data chain. - Other — Replaces event
payloadwith value from an<operationKey>.
- Data of Last Operation — Replaces event
If you create items in a single request, the flow will trigger once for each item. If you create three items, the flow runs three separate times. On each run, just one item will be in the payload.
Filters
A filter will halt the event transaction, copy the event payload into the flow, let the whole flow run,
optionally replace the original payload by configuring the response body, then resume the event's transaction to
the database.
items.created scope, the item itself will not have an ID, as it hasn't been created yet.If no Response Body is configured, the original payload will not be modified, but you'd still have the ability to cancel the transaction.
To completely cancel a transaction, you'll need to throw an error within a script operation or end the Flow on a failure path.
Actions
An action lets the event commit its transaction to the database without waiting for the Flow to finish. These are asynchronous, leading them to be more performant, but without the ability to validate or transform the payload before the transaction is committed to the database. However, a copy of the payload is still added into $trigger to use as needed.
Webhook
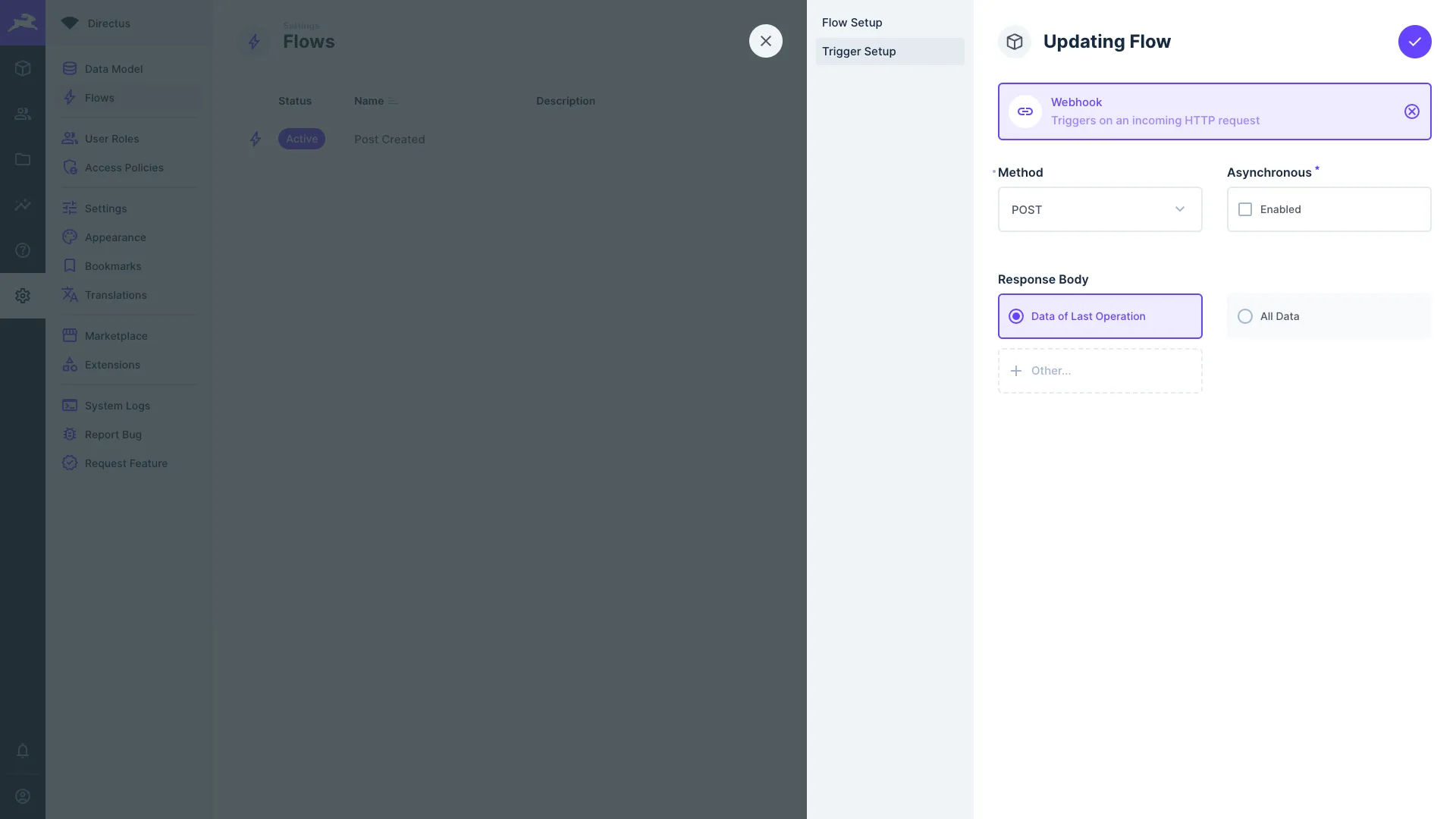
Webhooks are triggered on an incoming HTTP request to: /flows/trigger/:this-webhook-trigger-id which you can copy from the webhook
trigger panel.
- Method — Choose whether the Flow will be triggered by a
GETorPOSTrequest from the dropdown. - Asynchronous — Toggle whether or not the trigger responds asynchronously.
- Response Body — Optional. Defines data to return as a response. Choose to return:
- Data of Last Operation — Responds with value from
$last. - All Data — Responds with the entire data chain.
- Other — Responds with value from an
<operationKey>.
- Data of Last Operation — Responds with value from
- Error on Reject - Choose whether an error should be thrown if the final operation rejects.
- Cache — Choose whether responses to
GETrequests should be stored and served from cache or the cache should be bypassed.
If no data is defined in Response Body, the response is empty.
If Asynchronous is enabled, the Flows system will immediately resolve/respond to the request without returning a Response Body, which frees up the API immediately. If it is disabled, the Flows system will wait for the Flow to finish and return whatever value is in Response Body. This slows the API, but lets you send data.
Schedule (CRON)
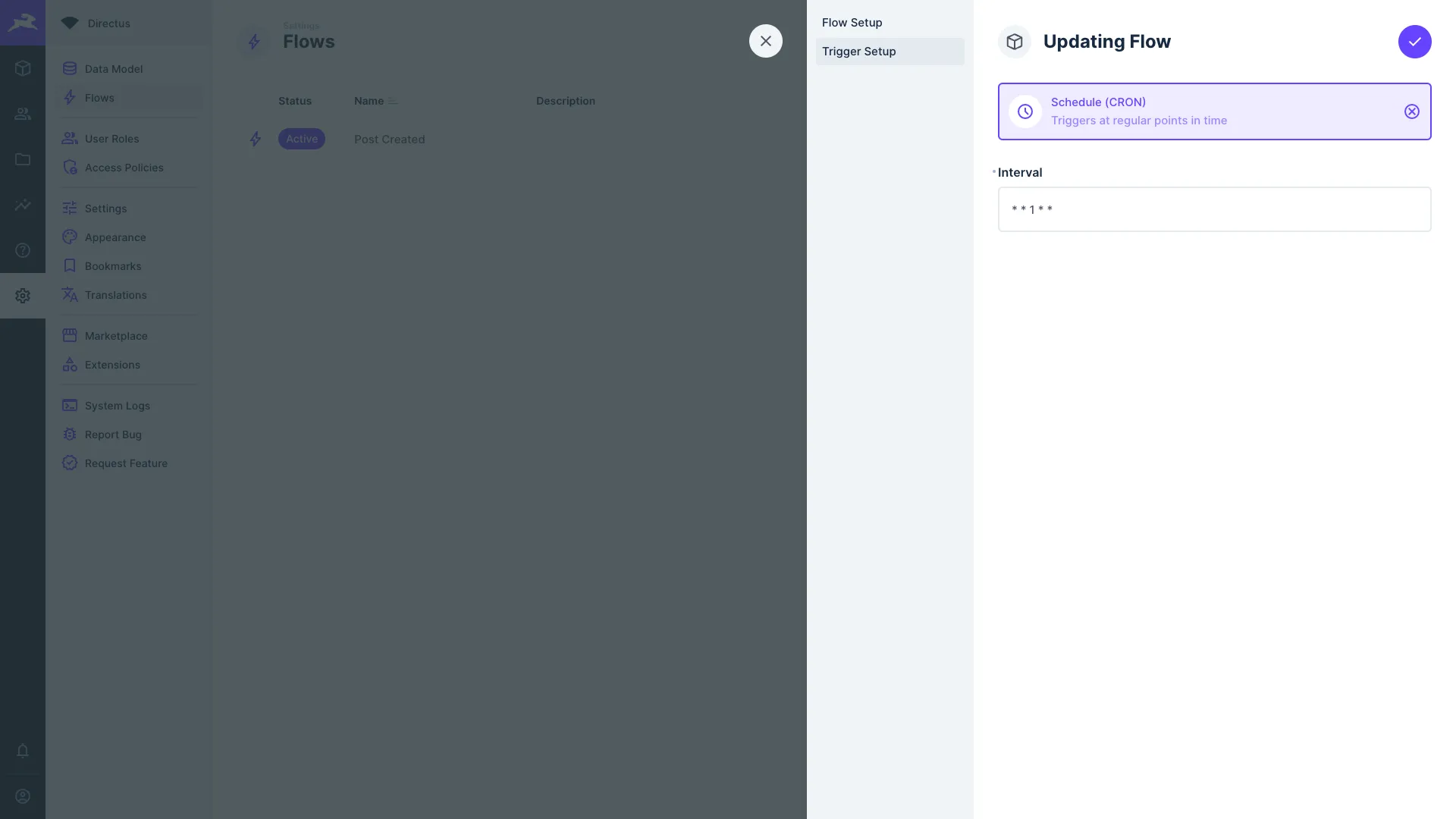
This trigger type enables creating data at scheduled intervals, via 6-point cron job syntax.
- Interval — Set the cron job interval to schedule when the Flow triggers.
Syntax Explanation
┌────────────── second (0-59)
│ ┌──────────── minute (0-59)
│ │ ┌────────── hour (0-23)
│ │ │ ┌──────── day of month (1-31)
│ │ │ │ ┌────── month (1-12)
│ │ │ │ │ ┌──── day of week (0-7)
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │
* * * * * *
Another Flow
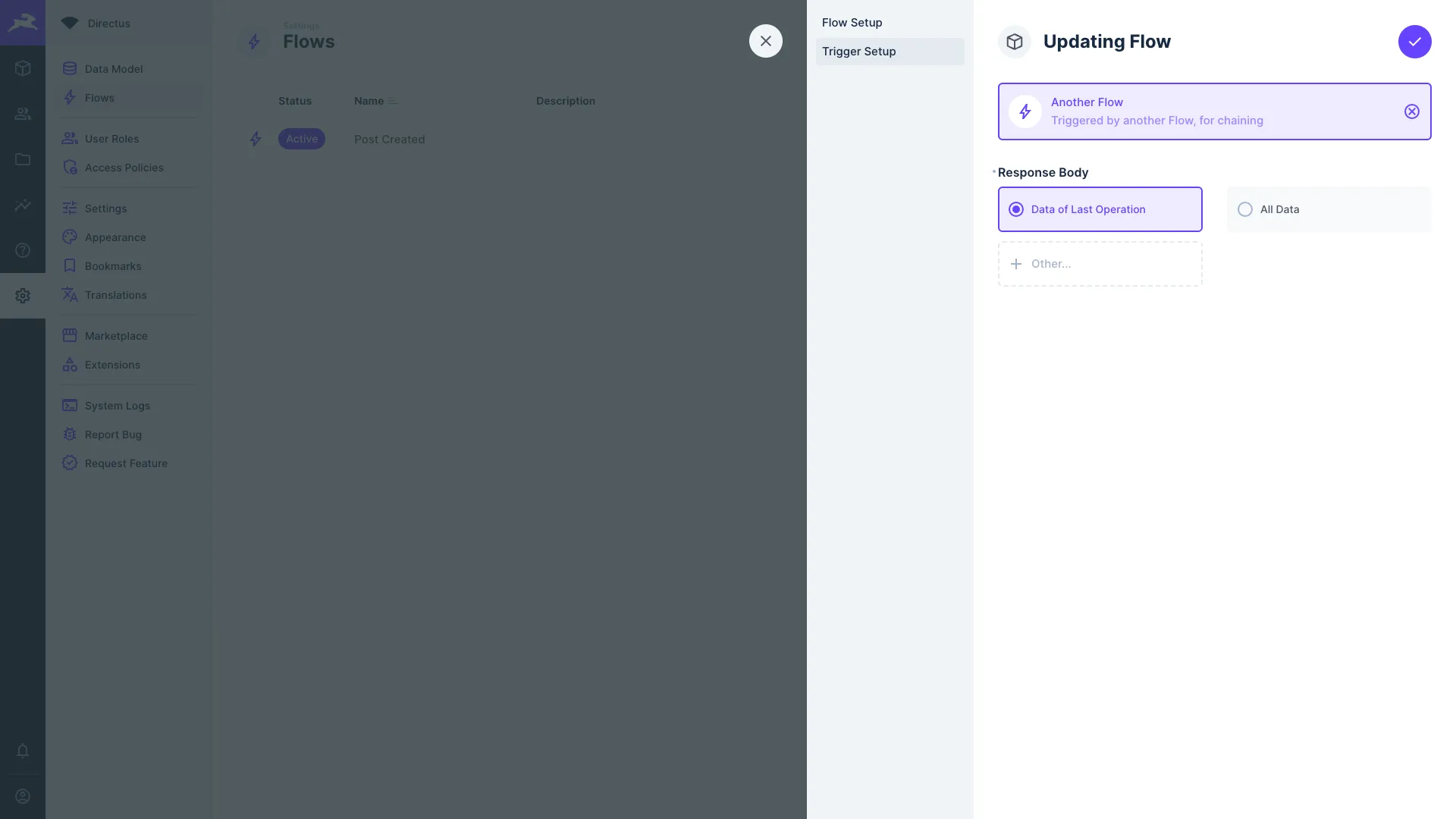
This trigger type executes by the trigger Flow operation, allowing chaining Flows.
- Response Body — Optional. Defines data to return and append under the
<operationKey>of the trigger Flow operation that tripped the trigger. Choose to return:- Data of Last Operation — Responds with value from
$last. - All Data — Responds with the entire data chain.
- Other — Responds with value from an
<operationKey>.
- Data of Last Operation — Responds with value from
If you pass an array to this trigger, it will run once for each item in the array.
Manual
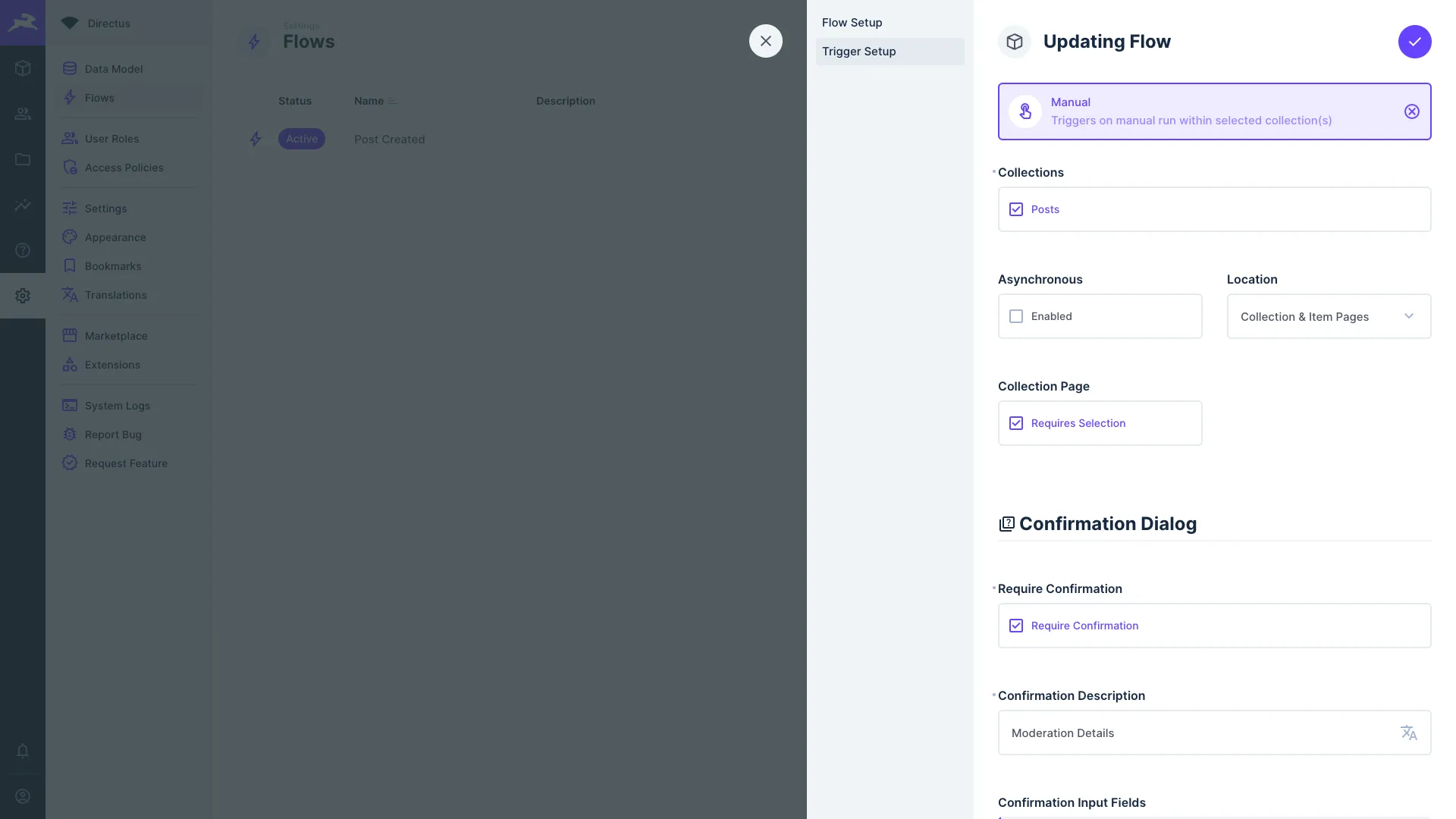
This trigger starts your Flow on a manual click of a button within the Data Studio.
The manual trigger must take in item ID(s) before you can click it. On the collection page, the button will be
grayed out until you select some number of items. From the item page, the current item's ID is passed in
automatically. These item IDs are passed in to $trigger as an array.
- Collections — Choose the Collection(s) to add the button to.
- Location — Choose to display the button on the Item Page, Collection Page, or both.
- Asynchronous — Toggle whether the Flow executes asynchronously. If enabled, you can immediately trigger the Flow again. If not, you must wait for the Flow to complete to use it again.
- Collection Page (Requires Selection) — Toggle whether a selection is required in the Collection Page to trigger.
- Require Confirmation - Toggle whether a confirmation dialog will be shown before the Flow is executed.
- Error on Reject - Choose whether an error should be thrown if the final operation rejects.
After the operation runs, a toast notification will appear in your sidebar indicating whether the Flow ran successfully.
Confirmation Dialog
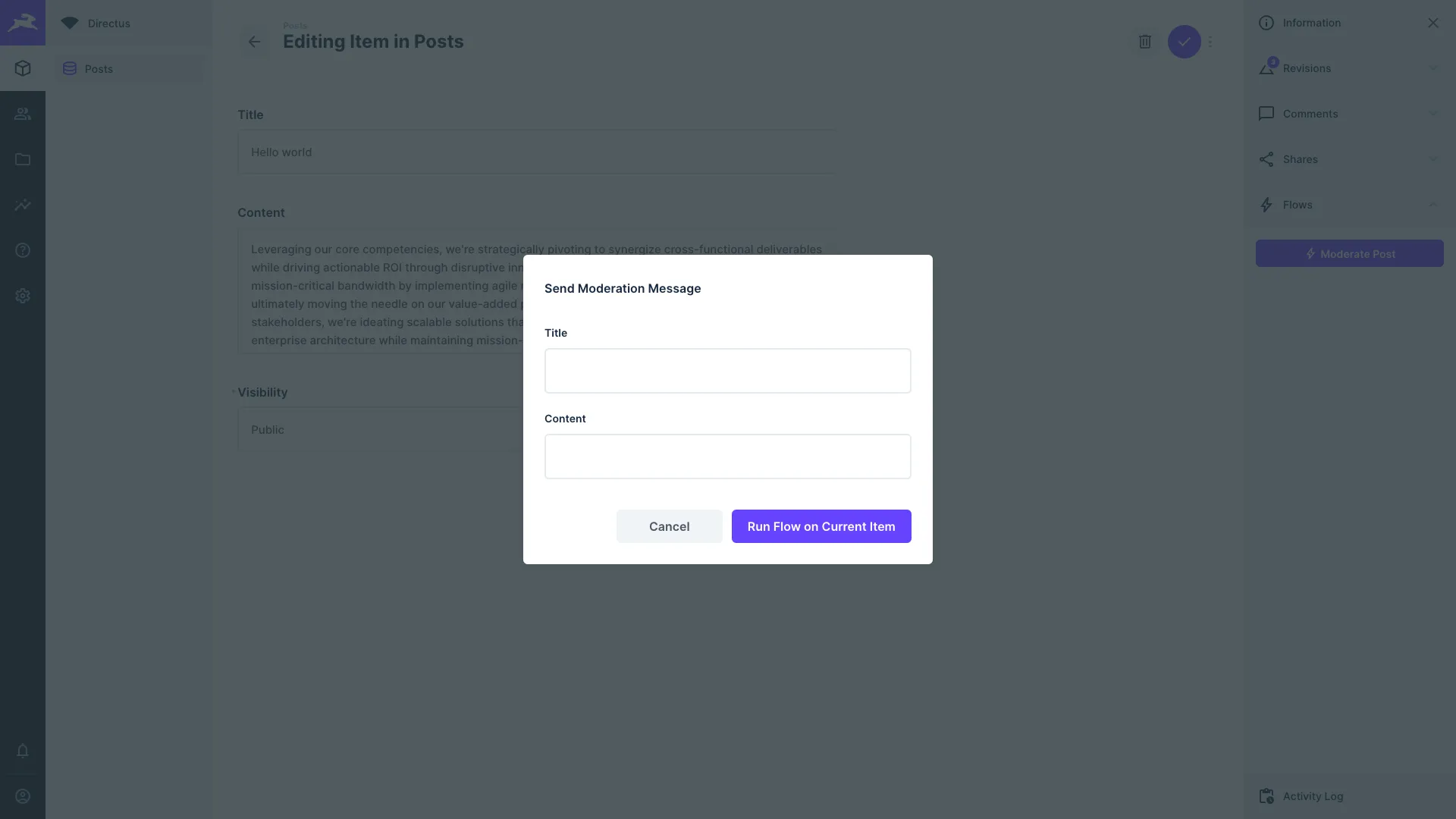
If enabled, a confirmation dialog will be shown in a modal before the Flow is executed. There are further options to set up a confirmation dialog.
- Confirmation Description - Text shown at the top of the modal.
- Confirmation Input Fields - Set up one or more inputs to be filled by users before executing the Flow.
Each input field can have its own data type, interface, and display options. Some convenience options are also provided to immediately alter the user input (such as trimming whitespace and slugifying text).
Data provided by users when triggering a manual Flow with a confirmation dialog will be accessible in $trigger.body in
the data chain.
Get once-a-month release notes & real‑world code tips...no fluff. 🐰