Fields
Fields are database columns with additional metadata and configuration used by Directus, such as how data is displayed, validations, and interfaces.
Types
Directus supports various databases, though each vendor has their own simple data types. To standardize these differences, Directus has a single set of types that are mapped to the vendor-specific ones.
| Group | Types |
|---|---|
| Text | String, Text, UUID, Hash, Alias |
| Numeric | Integer, Big Integer, Float, Decimal |
| Boolean | Boolean |
| Date and Time | Timestamp, DateTime, Date, Time |
| Binary | Binary |
| Structured | JSON, CSV |
| Geospatial | Point, LineString, Polygon, MultiPoint, MultiLineString, MultiPolygon |
Fields that do not map directly to an actual database column are called "alias" fields, and include presentational fields and certain relational fields.
Geospatial fields are used to store data in GeoJSON format. These types are only supported if your database supports spatial extensions.
Creating Fields
When creating a new field, you must first select an interface and provide some basic configuration. Basic configuration will depend on the interface selected, but all fields have some common characteristics.

The interface describes how users will create and edit data, as well as how it is displayed in Editor. There are many kinds of built-in interface, such as a text input, date selector, map, and a set of relationship interfaces. More interfaces can be built as extensions.
The key is the unique name for a field within a collection. This value is used in both the Data Studio and via API. Within the Data Studio, the key is parsed through our title formatter to improve readability.
The type defines the underlying data type configured in the database. When creating fields, the available types will correspond to the interface selected.
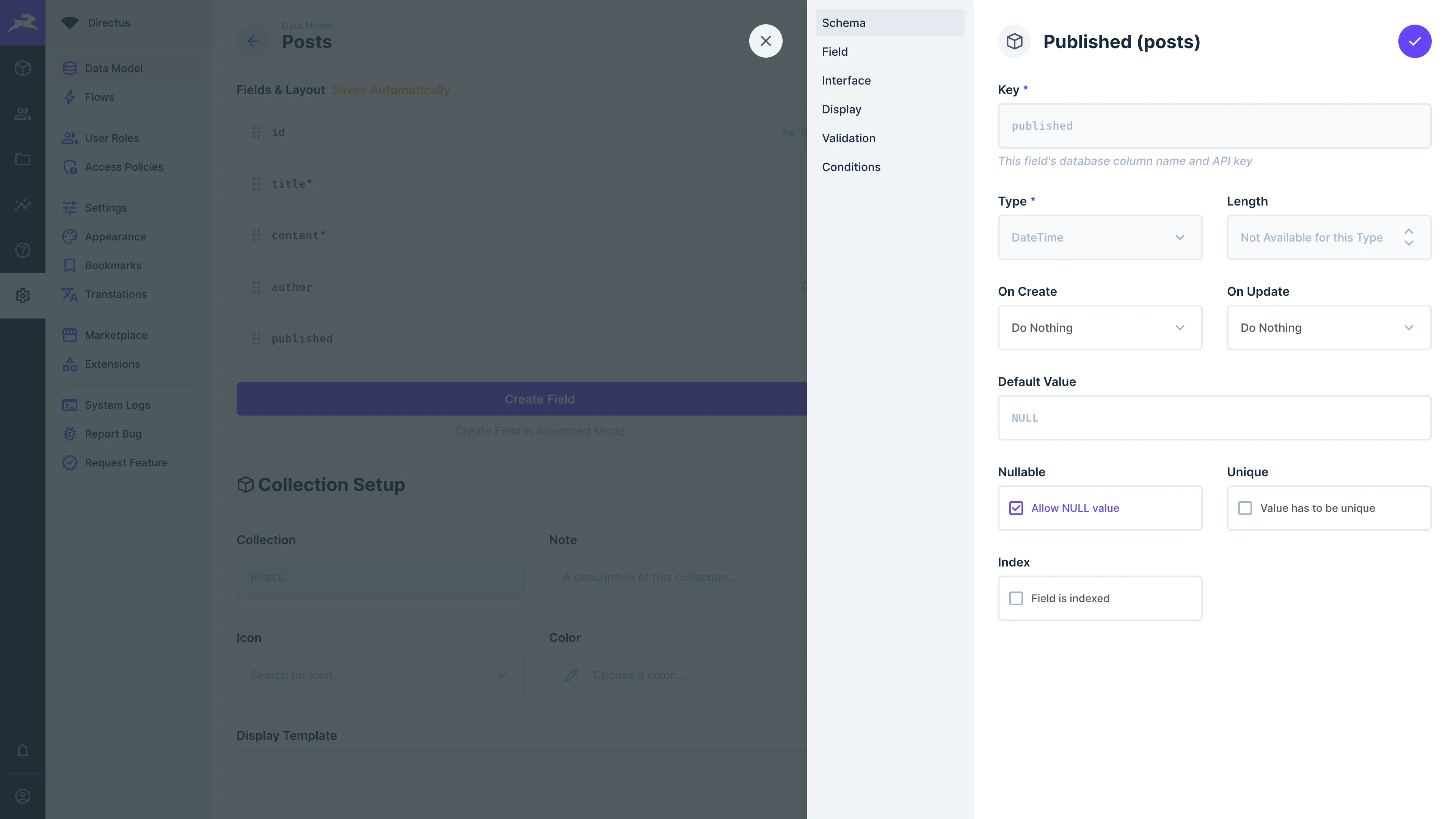
Configuring Fields
There are a number of advanced configuration options available for fields. Some must be configured at the time of creation, while others can be edited after creation.
Schema
This section defines the database column settings for the field. This includes the key, type, length (if applicable), default value, whether the field is nullable, whether values must be unique in the collection, whether the field is indexed, and whether or not to include the field in searches.
Field
This section sets details for the interface, which is displayed in the editor. This includes whether the field is read-only or requires a value to be provided when an item is created.
This section also allows for a note - which is displayed in the editor and provides additional context or help to the user, and field name translations, which changes the label of this field in the editor based on the selected language in the Data Studio.
Interface
This section describes how the user will create, edit, and view data in the editor, and are effectively different form inputs. Each interface will have its own configuration options.
Display
This section describes how individual field values will be displayed throughout the Data Studio. You can always choose to display the raw value, but you can display a formatted value instead. Each interface will have its own display options.
Conditional styles allow for different colors, icons, and text values to be used when the field data meets configured criteria.
Validation
This section allows for the configuration of rules to determine valid user input. If validation fails, you can also use this configuration section to write custom messages.
These validations apply to data added via Directus and are not database-level validations.
Studio (client-side) using the field rules. Once any reported errors are resolved and the item is submitted again, the request is sent to the Server. The Server then re-runs the validation rules, along with permission checks. Any validation errors from either step are displayed on the form.Conditions
This section alters the current field's configuration based on the values of other fields in the item. Conditional configuration include whether a field is read-only, hidden, or required, along with any editable interface-specific configuration.
true in the field settings. Then, create a condition with a rule checking the value of another field. The condition should set hidden to false.Relationships & Translations
This section will only appear when the field is relational, and describes the relationship between this field and other collections. Each relationship type will be shown differently, and where there is a junction collection you will be given the option to add a sort field on the collection.
Relational triggers configure what will happen to the relational field data when related values are deselected or deleted. This includes setting values to null, their default, or cascading/preventing the deletion.
Field Width
Each field can be configured to be half or full width in the editor. Two half-width fields can be placed next to each other. Additionally, a field can be configured to use up the full-width of the editor, expanding beyond the usual full-width container.
Field width is not in the field configuration, but can be set by clicking on in the collection data model page.
halffields will go from[start]until[half]in the grid system, but have a maximum width of380pxdefined by the--form-column-max-widthcss variable.fullfields will be the sum of 2halffields, with a maximum width of760px.fillfields will fill the available space, without any maximum.
Field Data Attributes
Each field in the Data Studio includes data attributes that expose the underlying data model information:
data-collection- The collection namedata-field- The field namedata-primary-key- The item ID
These attributes enable programmatic field identification for custom styling, extensions, automated testing, and custom tooling.
<div data-primary-key="1"
data-collection="books"
data-field="name">
<!-- Field UI -->
</div>
System Collection Fields
System collections have a number of default fields that cannot be configured as they are required for Directus to operate. However, additional fields can be added to any system collection.
Existing Database Fields
When Directus is connected to an existing database, fields of supported types will be automatically made available in Directus. You can then fully configure it as desired within the Data Studio.
Get once-a-month release notes & real‑world code tips...no fluff. 🐰
Collections
Directus collections help you manage your data. Create custom collections, define fields, configure relationships, and leverage features like content versioning and access control. Learn how to create, configure, and manage collections in Directus.
Interfaces
Manage your data effectively with Directus fields. Discover various field types, interfaces, validations, and relationships to perfectly suit your data modeling needs.