Implementing Multilingual Content using Directus and Astro
Directus comes with built-in support for creating multilingual content. In this tutorial, you'll learn how to create multilingual content and access it using your Astro application.
Before You Start
You will need:
- A Directus project with admin access.
- Fundamental understanding of Astro concepts.
- Optional but recommended: Familiarity with data modeling in Directus.
Set Up Your Directus Project
Create a Collection
Create a new collection called posts with the following fields:
title(Type: Input)slug(Type: Input)content(Type: Markdown)
Edit Public Policy
To make your posts publicly accessible, navigate to Settings -> Access Policies -> Public. Then, under the posts section, set a public policy for Read.
For more details on how to set up access control and permissions, read the access control documentation.
Set Up Content Translations
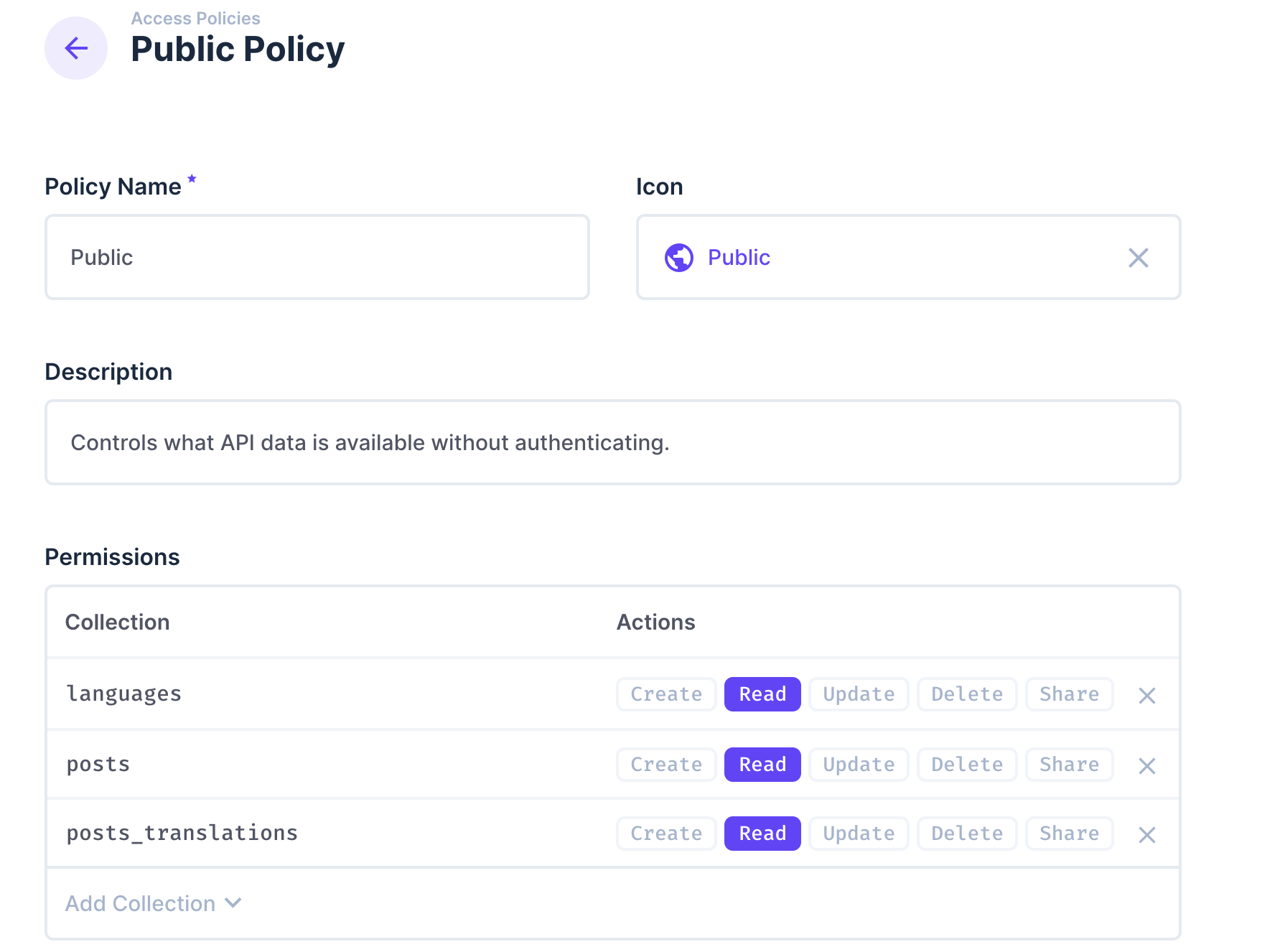
To enable multilingual support, start by adding a field named translations to the posts collection. Set its type to Translations, which will automatically generate two new collections: languages and posts_translations. Don't forget to allow Read access for the Public policy for these collections as well.
- Open the
posts_translationscollection, and add the fieldstitleandcontentwith their corresponding types. - Create post content with the according translations in 3 languages
Next, ensure that the Public policy allows Read access for both the languages and posts_translations collections.
Once the posts_translations collection is created, add the title and content fields, defining their corresponding data types.
Finally, add some content to the posts collection with the appropriate translations in three languages.
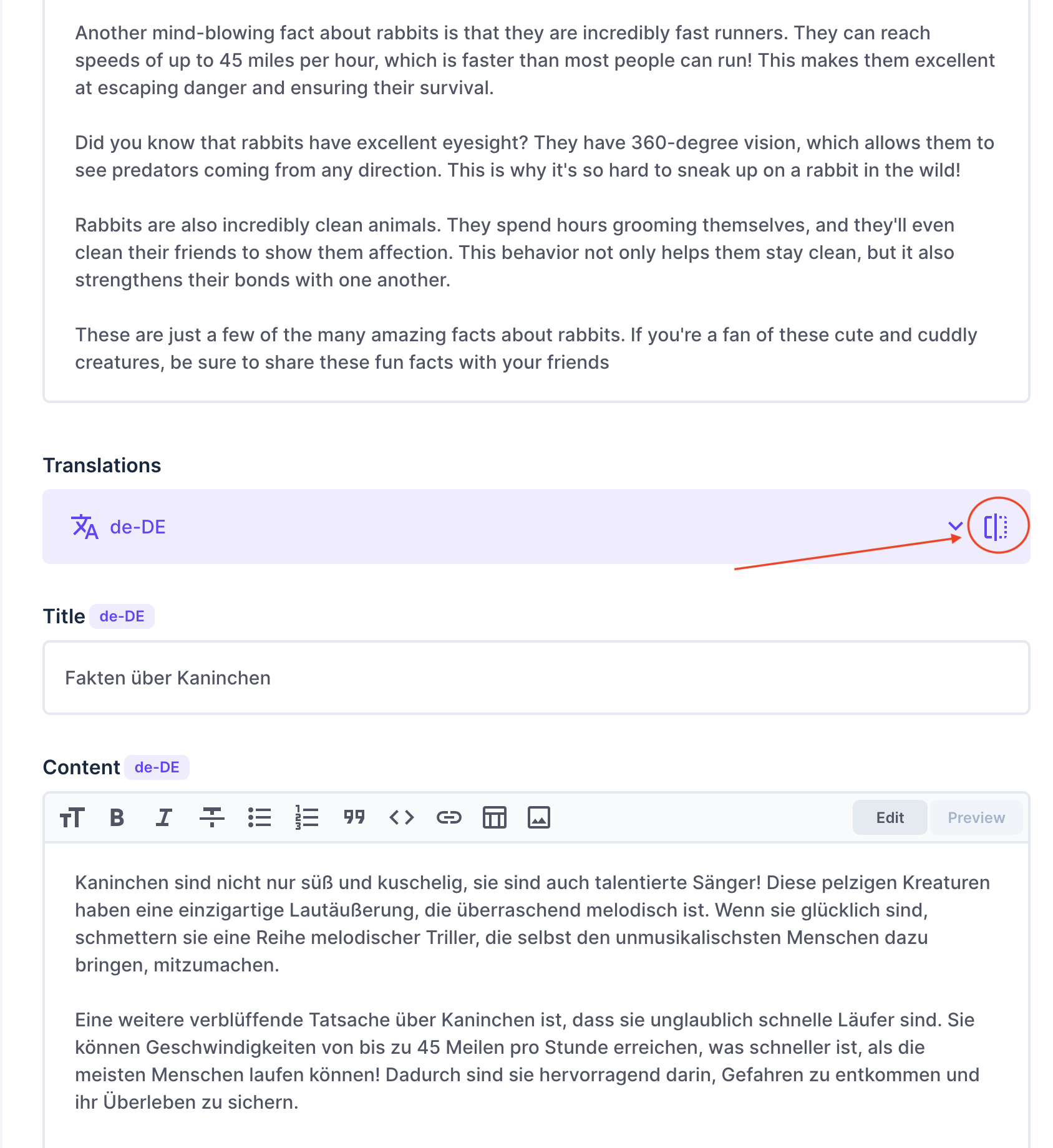
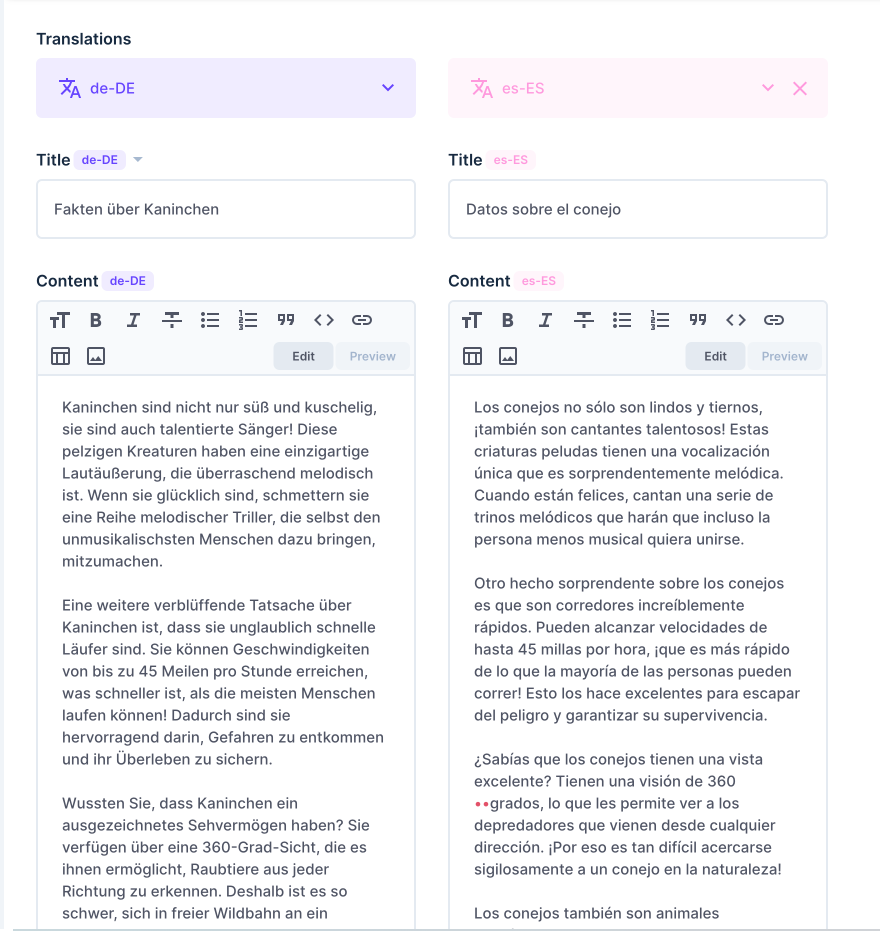
Clicking the Toggle split view to show the various translations of the content side by side.
Set Up Your Astro Project
Initialize Your Project
Create a new Astro project by running the command:
npx create-astro@latest astro-multilang
When prompted, select the following configurations:
How would you like to start your new project? A basic, minimal starter (recommended)
Install dependencies? (recommended) Yes
Initialize a new git repository? (optional) No
Navigate into the project directory and install the Directus SDK by running the command:
npm install @directus/sdk
Run the command npm run dev to start the development server and you should see the Astro project running on http://localhost:4321/ in your browser.
Configure the Directus SDK
First, create a .env file in the root of your project and add the following environment variables:
DIRECTUS_URL=https://your-directus-project-url.com
In the src directory, create a new directory called lib, and inside the directory, create a file called directus.ts. Add the following code to the file:
/// <reference types="vite/client" />
import { createDirectus, rest, readItems } from '@directus/sdk';
const DIRECTUS_URL = import.meta.env.DIRECTUS_URL;
const client = createDirectus(DIRECTUS_URL).with(rest());
export async function fetchPosts(lang: string) {
return await client.request(
readItems("posts", {
fields: ["slug", { translations: ["*", "languages_code"] }],
deep: {
translations: {
_filter: { languages_code: { _eq: lang } },
},
},
})
);
}
export default client;
The code above:
- Imports the Directus SDK and creates a client instance.
- Creates a function
fetchPoststhat fetches posts based on the language passed as an argument. - When fetching posts, it performs a deep query to get the translations posts based on the language passed.
You will use the fetchPosts function to fetch posts later in this tutorial.
Set Up Language-Based Dynamic Routing
Let's set up dynamic routing based on the language selected by the user making sure that whenever a user navigates to a post, the content is displayed in the selected language.
Before you do that, delete the Welcome.astro component in the components directory and the index.astro file in the pages directory as you do not need it for this tutorial.
Create a Navigation Menu
In the Layout.astro file in the layouts directory, update it to include a navigation menu:
---
const { lang } =Astro.props
---
<!doctype html>
<html lang={lang}>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
<link rel="icon" type="image/svg+xml" href="/favicon.svg" />
<meta name="generator" content={Astro.generator} />
<title>Astro Basics</title>
</head>
<body>
<nav>
<a href="/en-US/">English</a> |
<a href="/de-DE/">Deutsch</a> |
<a href="/es-ES/"> Espanol</a>
</nav>
<slot />
</body>
</html>
<style>
html,
body {
margin: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
Next, let's list all posts in the selected language and display the post content in the selected language.
List All Posts
In the pages directory, create a new directory called [lang], and inside the directory, create a file called index.astro with the content:
---
import Layout from "../../layouts/Layout.astro";
import { fetchPosts } from "../../../lib/directus";
const { lang } = Astro.params;
export function getStaticPaths() {
const supportedLanguages = ["en-US", "de-DE", "es-ES"];
return supportedLanguages.map((lang) => ({ params: { lang } }));
}
// Fetch posts for the selected language
const posts = await fetchPosts(lang);
---
<Layout lang={lang}>
<h1>Blog Posts in {lang}</h1>
<ul>
{posts.map((post) => {
const t = post.translations[0];
return (
<li>
<a href={`/${lang}/${post.slug}/`}>{t?.title}</a>
</li>
);
})}
</ul>
</Layout>
The code above gets the current lang the user is trying to access from the Astro.params object and fetches all posts in the selected language.
Since this is happening using the getStaticPaths function, Astro will generate static pages for each language and list all posts in the selected language.
Navigate to http://localhost:4321/de-DE/ and you will be provided you with a UI that looks like this:

Display Single Post Content
Inside of the [lang] directory, create a new file called [slug].astro with the content:
---
import Layout from "../../layouts/Layout.astro";
import { fetchPosts } from "../../lib/directus";
export async function getStaticPaths() {
const supportedLanguages = ["en-US", "de-DE", "es-ES"];
// Fetch all posts from Directus for each language
const posts = await Promise.all(
supportedLanguages.map((lang) =>
fetchPosts(lang).then((posts) =>
posts.map((post) => ({ params: { lang, slug: post.slug }, props: post }))
)
)
);
// Flatten the array to return all language + slug combinations
return posts.flat();
}
const { lang, slug } = Astro.params;
const post = Astro.props;
const t = post.translations[0]; // Get the correct translation
---
<Layout lang={lang}>
<h1>{t?.title}</h1>
<div set:html={t?.content} />
</Layout>
The code above:
- First gets the language and slug from the URL and create static pages for each language and post slug combination.
- Renders the post title and content in the selected language.
Navigate to http://localhost:4321/de-DE/rabbit-facts/ would provide you with a UI that looks like this:

Switching to a different languages would display the content in the selected language:

That's it! You have successfully implemented multilingual content using Directus and Astro.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how to create multilingual content in Directus and access it using your Astro application. You also learned how to set up language-based dynamic routing to display content in the selected language.
By following the steps outlined, you now have a solid foundation for building multilingual websites. You can expand this further by adding more languages, customizing the navigation menu, and enhancing the user experience with additional features like language switchers or automatic language detection.